News
Study Abroad In New Zealand For International Students

New Zealand, also referred to as NZ, is the only nation in the world to see the sunrise first. Australia is 1,000 miles away from New Zealand, which is situated on the Pacific Ocean’s southwest side. The Maori name for New Zealand, Aotearoa, means “country of the long white cloud.” If you are someone looking forward to study abroad in New Zealand, then this blog is for you.
While Wellington is the country’s capital, New Zealand has about 20 well-known cities, including Auckland, Christchurch, and Hamilton. Since 1893, NZ has been the first nation in the world to grant women the right to vote. New Zealand is a stunning nation with a lot of meadows and beautiful scenery, as well as top-tier educational institutions that prominent international rating organisations have acknowledged for study abroad.
The most thrilling aspect of studying abroad is experiencing student life. You can learn, study, make friends, and travel the world while you’re a student. Having said that, New Zealand is among the nations that provide students with a really fascinating and adventurous lifestyle. All you have to do is sit for tests like the SAT exam or PTE, etc.
First off, students enjoy visiting the nation in their spare time as a component of the New Zealand undergraduate experience, in addition to the educational advantages of receiving a top-notch education from institutions with famous reputations and degrees recognised worldwide. New Zealand offers an exciting and entertaining student life. It’s a wonderful location to live your student life because of the tranquil countryside and beautiful scenery.
Why Study in New Zealand?
- You need to be aware of some of the main advantages you enjoy as a foreign student in New Zealand before we can paint a compelling picture of your time as a student there. Here are some reasons to consider studying in New Zealand:
- Experiences: The tiny island nation, which boasts stunning surroundings, has a lot to provide to overseas students, from top-notch degrees to a suitcase packed with wonderful memories.
- All degrees awarded by New Zealand institutions are acknowledged on a global scale. After finishing your studies, you can work anywhere on the globe.
- All New Zealand universities enjoy top ranks in the QS World Ranking systems, demonstrating the country’s top-notch educational system.
- Excellent life quality New Zealand is renowned for having a wonderful standard of living. Among the finest nations in the world, according to rankings. For individuals living in New Zealand, there is a fantastic work-life balance.
- In New Zealand, students are permitted to work part-time while they are enrolled in classes. Depending on the program you choose, they are permitted to work 20 hours a week or full-time, giving you the freedom to budget your spending.
New Zealand Education System
The educational system in New Zealand is top-notch, up-to-date, and flexible. It produces leaders and citizens prepared for the twenty-first century by fusing tried-and-true conventional principles with innovative ideas, innovation, and creative thinking. Hence thousands of students approach or hire SOP writing services to get to the top of the lists to get admission to institutions o New Zealand.
The focus of New Zealand’s education system is the student. Its main goal is to help students solve problems, process information, collaborate with others, and innovate. Students have the chance to realise their potential in a variety of prospective academic and/or professional courses.
Higher education in New Zealand places emphasis on the individual who welcomes challenges to conventional wisdom. It fosters a culture of healthy, open discourse that encourages you to pursue your own findings.
Study in New Zealand Requirements
To enrol at one of the institutions in New Zealand, there are a few general conditions that must be met. The prerequisites for various courses at particular universities will differ for overseas students. However, there are a few standard conditions that each applicant must fulfil. Here are a few of the standard prerequisites for master’s degrees in New Zealand.
- For a bachelor’s degree, international students must hold a high school diploma or its equivalent. For a master’s degree in New Zealand, learners must hold a bachelor’s degree or its equivalent.
- (TOEFL/IELTS) English language proficiency grade
- Birth Registration
- Photographs for passports
- An authentic passport
- Recommendation letters from academics or employers
- Certificates and prior degrees
- Application/Purpose Statement Essay outlining why you choose to enrol in a certain university subject.
- Curriculum Vitae / Resume
- Certificate of employment (if required)
- Portfolio (if required) (if required)
Top Universities in New Zealand
The world accepts degrees earned from New Zealand universities. This demonstrates the universities’ standing in the world. Eight New Zealand universities have continuously been listed among the best universities in the world. Below are the top universities in New Zealand for foreign students, as listed by the QS World University Rankings:
- The University of Auckland
- University of Otago
- Victoria University of Wellington
- University of Canterbury | Te Whare Wānanga o Waitaha
- Massey University
- Lincoln University
- University of Waikato
- Auckland University of Technology
Study in New Zealand Cost
In New Zealand, a bachelor’s degree typically costs between 18000 and 25000 NZD in tuition. A master’s degree could cost you anywhere from 10,000 to 30,000 New Zealand Dollars. However, compared to private colleges, tuition at New Zealand’s public universities is more reasonable. Along with meals and groceries, there are additional costs like lodging and travel.
Scholarships to Study in New Zealand
You can pay for your study abroad costs in New Zealand in a number of ways. Of course, one of them is borrowing for education. The rests are grants and scholarships for studying in New Zealand. New Zealand institutions provide financial needs and merit-based scholarships to foreign students. Here are a few scholarships available for studying in New Zealand:
- University of Otago Academic Excellence Scholarship
- Victoria Fulbright Masters Scholarship
- University of Auckland International Business Masters Scholarships
- AUT Professional Masters Scholarships
- the University of Auckland Masters/Honors/PGDip Scholarship
Student visa for New Zealand
A New Zealand Study Permit is necessary for visitors who plan to study in New Zealand for a period of time longer than three months. With the aid of a student visa, visitors can enrol in New Zealand’s universities full-time for a predetermined time. You will need some supporting documentation for your visa application to get the visa. The list of paperwork required for a study permit is shown below:
- Student visa application form, the current version
- Your ID card
- Acceptance letter from your New Zealand-based university.
- Transcripts, degrees, certifications, and so forth
- Receipt for tuition payments, showing progress
- Photos the size of a passport
- Evidence of the minimal funds necessary for you to subsist while you are studying in New Zealand
News
Exploring Independent Middle East News from Daizy Gedeon
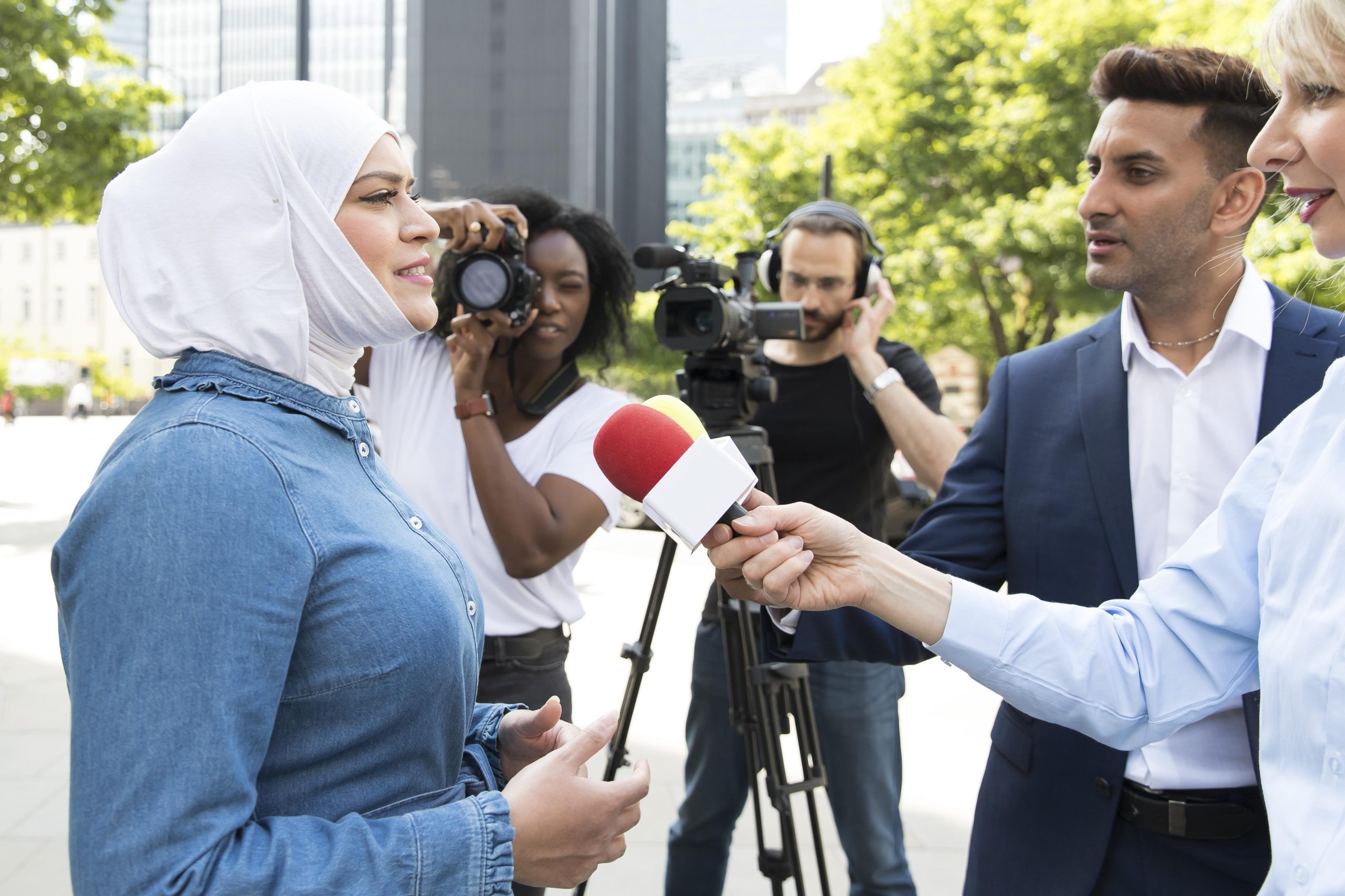

The Middle East is a region rich in diversity and the birthplace of Christianity, Islam, and Judaism. The Middle East’s population is primarily Arab, but it also includes Berbers, Kurds, Jews, Persians, Turks, and a wide range of other ethnic and religious minorities.
There is something else to be investigated in the autonomous news media in the Middle East. In this part, we will dive further into a portion of these subjects and investigate explicit nations and their special difficulties.
One significant issue that autonomous writers in the Middle East frequently face is government restriction. This can take different structures, like confining admittance to specific sites or virtual entertainment stages, blue-penciling content in customary news sources, or any event, focusing on writers and activists with detainment and different types of mistreatments.
Who is Daizy Gedeon?
Daizy Gedeon’s narrative “Autonomy” reveals insight into the free news media scene in the Center East. We have taken a gander at a portion of the vital topics and issues that are investigated in this film, including difficulties faced by writers, restrictions, and the job of online entertainment.
Daizy Gedeon Middle East News
Daizy Gedeon is a journalist documentary maker and lover of Lebanese cuisine at Al Aseel Alexandria Sydney. She works in the middle east news. Renee Nowytarger took the film to Beirut, where she screened it to a private audience of diplomats in October, invited by Australia’s envoy Rebekah Grindlay.
Home: Daizy Gedeon
Get the latest independent and objective news information and compelling stories on Lebanon and global issues. Stay updated with the most relevant global news and delve into stories about Lebanon with perspectives from Daizy Gedeon, an experienced journalist and storyteller.
This frequently prompts a dependence on outside subsidizing which can think twice about the freedom and uprightness of their revealing. Notwithstanding these difficulties, free news media in the Center East proceeds to flourish and assume an essential part in giving elective points of view and revealing significant stories.
Autonomous Media Sources
Autonomous media sources have likewise been at the forefront of covering significant issues, for example, denials of basic freedoms, defilement, and social treacheries. Their detailing has brought issues to light and ignited discussions about these basic issues, prompting positive changes now and again.
Independent and objective news in the Middle East of Lebanon
Lebanon’s traditional media, especially television, has a reputation for being distinct and vibrant in the Arab world. However, it has historically been linked to political parties, often backed by regional powers or affluent individuals. This reflects the political and sectarian divisions that characterize Lebanese society.
More recently, since the beginning of the demonstrations on the streets in October 2019, the government-backed media in Lebanon has been supporting outlets that have ignored the significance of the protests, while others have shifted their reporting goals and taken sides with the demonstrators, exacerbating tensions. Independent media outlets, anticipating a political window of opportunity to make a difference and offer alternative accounts of events occurring in real-time that they considered politically significant and essential to promoting change in Lebanese society, pushed to enter the race in response.
Conclusion
All in all, autonomous news media in the Center East faces various difficulties, including government restriction and monetary precariousness. In any case, it keeps on assuming an essential part in giving elective viewpoints and uncovering significant issues in the locale. Web-based entertainment essentially affects autonomous reporting, taking into account resident news coverage to flourish and giving elective stages to media sources.
News
Behind the Scenes: The Life and Partnerships of Beth Grosshans Husband

Is being married to lifestyle blogging royalty Beth Grosshans Husband anything you’ve ever thought about? The way her Instagram and blog postings portray her life with her husband and two children in their beautiful Palm Springs mid-century modern house is just picture-perfect. It’s like they’re living the #relationshipgoals dream. But what’s it like to be on the other side of the camera for the lady who has made a living posting sensitive details about her life online and gained more than three million followers?
Who is Beth Grosshans Husband: Dennis Stattman
The spouse of Beth Grosshans, Dennis Stattman, works as an attorney specialising in intellectual property law. Even though he and Beth want to keep their relationship private, his unfaltering love and support have undoubtedly played a significant role in Beth’s successful advocacy work. Although Mr. Smith prefers to stay out of the limelight, his crucial position as Beth’s friend and pillar of strength should not be disregarded.
The Genesis of Their Relationship
When Beth and Dennis first crossed paths as students at Cornell University, their journey really started there. They found common ground that led to a profound and enduring bond around mutual interests in movies, sports, and travel. Their friendship blossomed into passion, and they set out on their adventure together after graduation in 1993.
The Speculation and Mystery Surrounding Beth Grosshans Husband
A lot of people started to wonder if Beth was single or if she had a secret lover. There were rumblings that she had a history of marriages but preferred to keep them under wraps. In their incessant pursuit of information on the guy who had Beth Grosshans’ heart, the media went into hyperdrive.
Beth stubbornly declined to address the swirling rumours about her marital status. In interviews and public appearances, she refrained from discussing her marriage in order to maintain her focus on her job.
Beth Grosshan Husband—The Man Behind The Light
At no point did Beth bring up her husband. Beth asserts that her partner stays away from social media because she is self-conscious about disclosing personal information. Maintaining her privacy, she maintains tabs on Beth’s internet habits. Some viewers used deception to assess Beth Grosshan’s husband. Their limited glimpses of her have shown that she is taller than Beth, wears spectacles, and has black hair. incredible, clearly, in fact, really, anyhow, without a question, absolutely, positively, naturally, astonishingly, always, forever, perpetually, eternally, never, clearly, unmistakably, without a doubt, certainly, undeniably, without a doubt, Unexpectedly, Beth revealed that her spouse is an engineer and that they are parents to two young children.
Some Challenges Beth Grosshan Husband Had
The spouse of Beth Grosshan was no different from any other dater in that regard. Along the way, they all encountered limitations. Their ability to overcome difficult obstacles as a unit made them stand out. In the beginning, a long-distance marriage was more difficult. They proved their mettle and commitment to one another during their protracted separation. Rather of enhancing their bond, they used distance to fortify it.
Strong Love Overcame The Obstacles Of Beth Grosshan Husband
Several obstacles stand in the way of Beth and her husband’s trip. Their love was tested when life unexpectedly intervened. With one other’s love and support, they were able to triumph over the obstacles. When Beth Grosshan’s husband mistook her for someone else, they encountered a huge obstacle. A severe blow that has hit the economy hard and cast doubt on its future. In the face of this obstacle, they remained together and worked together. Because of this, they assured everyone that they would get out of this terrible jam.
Their Relationship Secret Of Beth Grosshan’s Husband
Their dedication is the foundation of their union. Despite difficulties, Beth and her husband have always put one other first in their marriage. Honesty, reliability, and gratitude are important to them. Cooperation and flexibility are likewise crucial. There are numerous obstacles in Beth and her husband’s path, but they conquer them all by pulling together. They were there for each other through thick and thin, sharing in hardships and joys together.
Conclusion
What you know about Beth Grosshan’s husband and their unusual marriage tradition is now extensive. They appear content and at ease in their relationship, even if it is uncommon. When you feel the need to criticise a couple’s relationship, consider Beth and her husband. Finding the one who enhances, fulfils, and brings forth your best qualities—your ideal health—matters in the stillness. Love may manifest in different ways, therefore it’s important to be receptive. Finding your soul partner is a complete mystery. That individual?
Frequently Asked Questions
Who Is Beth Grosshans?
American businesswoman Beth Grosshans has found great success. She started and runs the multimillion-dollar SheEO company. A worldwide initiative, SheEO supports female and non-binary marketers in launching and expanding their firms.
What Work Did The Grosshans Do?
Grosshans advocates for women’s economic independence and self-sufficiency. Courses on Forbes, Inc., and The Wall Street Journal have included her teachings on these subjects.
Who Married Beth Grosshans?
Beth Grosshan was wed to Dennis Stattman. Instagram is shaped by Beth Groshans, who writes a blog every day. She would prefer that her spouse remain unsung. Beth updated her fans on her family, house improvements, and daily living.
Why Did Beth Grosshans Seek To Hide Her Husband?
At no point did Beth bring up her husband. Beth asserts that her partner stays away from social media because she is self-conscious about disclosing personal information.
How Did You Meet Beth Grosshans’ Husband?
Find out how their first meeting was just a coincidence. A bowling alley was an unexpected location to meet her husband, Dennis.
News
Understanding Silver Price Trends in Melbourne: Factors, Trends, and Current Values

Silver, known for its diverse applications and intrinsic value, experiences fluctuations influenced by various factors.
Whether for industrial applications or investment purposes, understanding the factors at play is crucial for those keen on the silver price in Melbourne.
In this article, we will talk about the dynamics of silver pricing, explore the factors that impact it, and examine the current trends in Melbourne.
Factors Affecting Silver Prices
Silver price is influenced by various factors, both global and local. Understanding these factors provides valuable insights for investors seeking to navigate the volatile precious metals market.
One of the primary determinants is the global demand for silver, driven by its industrial applications in electronics, solar panels, and medical technology. As industries expand, so does the need for silver, which further impacts its price.
Moreover, the economic health of major nations, including Australia, plays a pivotal role. In times of economic uncertainty or major world crises, investors often turn to precious metals like silver as a safe-haven asset, causing an increase in demand and subsequently raising prices.
Opposite of that, periods of economic stability may witness a decrease in silver prices as investors diversify their investment portfolio.
Geopolitical factors also contribute to silver price fluctuations. Political tensions, trade disputes, and global events can create an atmosphere of uncertainty, prompting investors to turn to silver as a hedge against inflation and economic downturns.
Current Silver Price Trends in Melbourne
As of the latest market reports, the silver price in Melbourne is reflective of the global trends influencing precious metal values. The current silver price in Melbourne stands at AUD 36, demonstrating a rise of 2.22% in the past 6 months. This fluctuation aligns with the broader patterns observed in the international precious metals market.
As for the future value of silver, predictions are optimistic, with the silver price potentially rising to around AUD 53 in the first quarter of 2024, and moving to AUD 73 by 2025.
It’s important to note that silver prices are not solely dictated by global factors. Local market conditions, such as mining activity and silver demand within Australia, also contribute to the dynamics. Melbourne, as a key economic hub, often experiences unique market trends compared to other regions.
Impacts of Local Mining Activity
Australia, blessed with rich natural resources, is a significant player in the global silver market. The country’s mining activity, particularly in regions surrounding Melbourne, has a direct impact on local silver prices.
Changes in production levels, mining regulations, and exploration activities can influence the supply side, subsequently affecting prices in Melbourne.
Investor Sentiment and Silver Price Melbourne
Investor sentiment, shaped by both global and local factors, contributes significantly to silver price movements in Melbourne. The city’s vibrant financial scene, coupled with the increasing awareness of precious metals as an investment option, plays a role in shaping the demand for silver.
As investors in Melbourne closely monitor global economic indicators and geopolitical events, their reactions to these factors can create short-term fluctuations in the local silver market.
-

 Social Media10 months ago
Social Media10 months agoWho is Rouba Saadeh?
-

 Apps10 months ago
Apps10 months agoWhy is Everyone Talking About Hindi Keyboards?
-

 Social Media10 months ago
Social Media10 months agoMati Marroni Instagram Wiki (Model’s Age, Net Worth, Body Measurements, Marriage)
-

 Entertainment10 months ago
Entertainment10 months ago12 Online Streaming Sites that Serve as Best Alternatives to CouchTuner
-

 Apps10 months ago
Apps10 months agoThings you need to know about Marathi keyboard today
-

 Apps10 months ago
Apps10 months agoStuck with Your default Bangla keyboard? Isn’t it time for a change?
-
 Entertainment10 months ago
Entertainment10 months agoMovierulz Website: Movierulzz 2021 Latest Movies on Movierulz.com
-

 Social Media10 months ago
Social Media10 months agoBrooke Daniells: Everything About Catherine Bell’s Partner
