Press Release
Lapis Lazuli: What Are The Negative Effects? – Guest Blog News
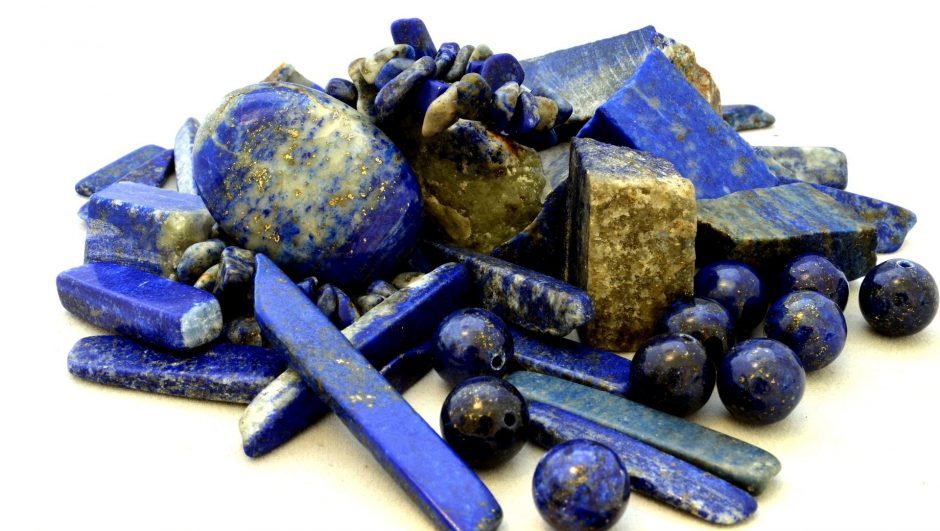

Lapis Lazuli is a blue, semiprecious stone that has been used by ancient civilizations for centuries. It is typically mined in Afghanistan, but there are some deposits in other areas of the world. In this article, we will discuss the potential health and environmental effects of Lapis Lazuli and its mining.
What is Lapis Lazuli?
Lapis lazuli is a blue semiprecious stone that has been used for centuries in jewelry and other decorative objects. While it is generally considered to be a positive and lucky stone, there are some negative effects associated with lapis lazuli as well.
Negative Effects of Lapis Lazuli
Lapis lazuli is a rock that has been used for centuries for its unique blue color. However, recent studies have shown that lapis lazuli may have negative effects on health. Some of the potential negative effects of lapis lazuli include:
1. Allergic reactions: Some people may be allergic to lapis lazuli, and can experience symptoms such as itching, swelling, and difficulty breathing.
2. Toxicity: Lapis lazuli contains small amounts of lead and other toxins, which can be harmful if ingested or inhaled.
3. Skin irritations: Lapis lazuli can cause skin irritations in some people, especially if it is not properly diluted.
4. Negative energy: Some people believe that lapis lazuli emits negative energy, which can be detrimental to one’s health and wellbeing.
If you are considering using lapis lazuli, it is important to be aware of these potential negative effects. You should also consult with a healthcare professional to see if lapis lazuli is right for you.
How to use Lapis Lazuli
Lapis lazuli is a beautiful blue gemstone that has been used for centuries in jewelry and other decorative objects. While it is generally considered to be a positive stone, there are some negative effects associated with lapis lazuli that should be considered before using it.
The most common negative effect of lapis lazuli is its potential to cause skin irritation. Some people develop an allergic reaction to the stone, which can lead to rashes, hives, and swelling. If you are prone to allergies, it is best to avoid contact with lapis lazuli.
In addition, lapis lazuli can also absorb negative energy. If you are feeling stressed or depressed, wearing lapis lazuli jewelry or carrying the stone with you can help to absorb some of the negativity. However, if you are already feeling negative, lapis lazuli can make the problem worse. It is important to be aware of your own energy levels and moods before using this stone.
Finally, lapis lazuli is thought to have psychic properties. While some people find these properties helpful, others may find them intrusive or overwhelming. If you are sensitive to psychic energies, it is best to avoid using lapis lazuli.
Alternatives to Lapis Lazuli
Lapis lazuli is a semiprecious stone that has been used for centuries in jewelry and other decorative items. However, lapis lazuli is not without its drawbacks. Some of the negative effects of lapis lazuli include:
Allergies: Some people may be allergic to lapis lazuli. Symptoms of an allergic reaction can include itching, swelling, and redness.
Toxicity: Lapis lazuli can contain high levels of lead and other toxic heavy metals. Ingesting even small amounts of these toxins can lead to serious health problems.
Cost: Lapis lazuli can be quite expensive, especially if it is of high quality. This cost can deter some people from using lapis lazuli in their projects.
There are several alternatives to lapis lazuli that can be used in its place. These alternatives include:
Glass: Glass is a cheaper alternative to lapis lazuli that can be found in many different colors and sizes.
Plastic: Plastic is another inexpensive alternative to lapis lazuli that can be found in a variety of colors and sizes.
Wood: Wood is a sustainable material that can be stained or painted to resemble lap
Press Release
Microsoft fumbles supply chain and acknowledges signing rootkit malware.

As of right now, Microsoft has admitted to signing a malicious driver that is disseminated in gaming contexts.
This “Netfilter”-named driver is actually a rootkit that has been seen interacting with Chinese C2 IP addresses.
Last week, the whole infosec. community joined G Data malware specialist Karsten Hahn in tracking down and analysing the malicious drivers that bore the Microsoft logo.
This incident exposed vulnerabilities to software supply-chain security once more, but this time it was caused by a flaw in the code-signing procedure used by Microsoft.
Rootkit “Netfilter” driver is Microsoft-signed.
A Microsoft signed driver dubbed “Netfilter” was detected last week by G Data’s cybersecurity alert systems as what at first glance appeared to be a false positive, but wasn’t.
The driver in question was observed interacting with C&C IPs based in China, which had no valid functionality and raised red flags.
This is when Karsten Hahn, a malware analyst at G Data, disclosed this publicly and contacted Microsoft at the same time:
Since Windows Vista, all code that operates in kernel mode must be tested and certified before being made available to the public in order to maintain the stability of the operating system.
According to Hahn, “Drivers without a Microsoft certificate cannot be deployed by default.”
At that time, BleepingComputer started tracking C2 URL behaviour and approached Microsoft for a comment.
A list of further routes (URLs), denoted by the pipe (“|”) symbol, are returned by the first C2 URL:
Each of these, in Hahn’s opinion, has a function:
The URL that ends in “/p” refers to proxy settings, “/s” offers encoded redirection IPs, “/h?” is for getting CPU-ID, “/c” offered a root certificate, and “/v?” refers to the malware’s self-updating capabilities.
For instance, as observed by BleepingComputer, the malicious Netfilter driver in question (residing at “/d3”) was accessible via the “/v?” path at the following URL:
After thoroughly examining the driver, the G Data researcher came to the conclusion that it was malware.
In a thorough blog post, the researcher examined the driver, its ability to self-update, and Indicators of Compromise (IOCs).
According to Hahn, the sample features a self-update routine that transmits its own MD5 hash to the server via the URL hxxp:/110.42.4.180:2081/v?v=6&m=.
An illustration of a request would be as follows:
hxxp:/110.42.4.180:2081/v?v=6&m=921fa8a5442e9bf3fe727e770cded4ab
“The server then replies with either ‘OK’ if the sample is current or the URL for the most recent sample, such as hxxp:/110.42.4.180:2081/d6. As a result, the malware replaces its own file “further information from the researcher
Other malware specialists like Johann Aydinbas, Takahiro Haruyama, and Florian Roth worked with Hahn during his analysis.
Roth has offered YARA rules for recognising them in your network environments after being able to compile the list of samples in a spreadsheet.
Microsoft is looking at a bad actor who spreads harmful drivers inside of gaming environments.
“In order to be certified by the Windows Hardware Compatibility Program, the actor supplied drivers. A third party created the drivers.”
Microsoft stated yesterday, “We have stopped the account and checked their uploads for additional indicators of malware.”
Microsoft claims that the threat actor primarily targeted the gaming industry in China with these malicious drivers and that there is currently no evidence that enterprise environments have been impacted.
Microsoft is waiting before blaming nation-state actors for this incident.
Sophisticated threat actors may take advantage of falsely signed binaries to help launch extensive software supply-chain attacks.
A well-known event in which code-signing certificates were taken from Realtek and JMicron to assist the comprehensive Stuxnet attack on Iran’s nuclear programme.
However, this specific instance has shown flaws in a reliable code-signing procedure, which threat actors have exploited to obtain Microsoft-signed code without jeopardising any certifications.
Press Release
FlexBooker reports a data breach, affecting more than 3.7 million accounts.

In an attack just before the holidays, the accounts of over three million customers of the American appointment scheduling service FlexBooker were taken, and they are now being exchanged on hacker forums.
The same hackers are also selling databases they claim to be from two other organisations: the Australian case management system rediCASE and the racing media outlet Racing.com.
Holiday breaches before
A few days before Christmas, there were supposedly three breaches, and the intruder posted the information on a hacking forum.
A popular programme for booking appointments and syncing employee calendars, FlexBooker, appears to be the source of the most recent data dump.
Owners of any company that needs to plan appointments, such as accountants, barbers, doctors, mechanics, lawyers, dentists, gyms, salons, therapists, trainers, spas, and the list goes on, are among FlexBooker’s clients.
The group claiming responsibility for the attack appears to go by the name of Uawrongteam, and they published links to files and archives containing personal information, including pictures, driver’s licences, and other IDs.
The database, according to Uawrongteam, has a table with 10 million lines of client data, including everything from payment forms and charges to pictures taken for driver’s licences.
Names, emails, phone numbers, password salt, and hashed passwords are among the database’s “juicy columns,” according to the actor.
Customers of FlexBooker have received a data breach notification that confirms the attack and that data on the service’s Amazon cloud storage system was “accessed and downloaded” by the intruders.
The letter states that “our account on Amazon’s AWS servers was compromised on December 23, 2021, starting at 4:05 PM EST,” adding that the attackers did not obtain “any credit card or other payment card information.”
FlexBooker advised consumers to be on the lookout for strange or fraudulent activities, and to monitor account statements and credit reports.
For further information, the developer also directed users to a report on a distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attack. It was then determined that some customers’ personal information had been obtained by the hackers.
The FlexBooker assault exposed email addresses, names, partial credit card information, passwords, and phone numbers for more than 3.7 million users, according to the data breach reporting service Have I Been Pwned.
Prior to FlexBooker, the threat actor known as Uawrongteam distributed links to material that was purportedly taken from Racing.com, a digital television station that broadcasts horse racing and offers news, stats, and event calendars associated with the sport.
The data from the Redbourne Gang’s rediCASE Case Management Software, which is utilised by numerous enterprises in addition to health and community agencies, looks to be another target of the same group.
Press Release
Rapyd, a “fintech-as-a-service” provider, to acquire Iceland-based Valitor, which establishes in-store and on the internet payments technologies, for $100M (Omar Faridi/Crowdfund Expert).

Rapyd, a “fintech-as-a-service” provider, to acquire Iceland-based Valitor, which develops in-store and online payments technologies, for $100M (Omar Faridi/Crowdfund Insider)
Omar Faridi / Crowdfund Insider:
Rapyd, a “fintech-as-a-service” provider, to acquire Iceland-based Valitor, which develops in-store and online payments technologies, for $100M — – Twitter- Facebook- LinkedIn- Pinterest- Reddit- HackerNews- Telegram- Weibo- Email- Print- Subscribe
-

 Social Media10 months ago
Social Media10 months agoWho is Rouba Saadeh?
-

 Apps10 months ago
Apps10 months agoWhy is Everyone Talking About Hindi Keyboards?
-

 Social Media10 months ago
Social Media10 months agoMati Marroni Instagram Wiki (Model’s Age, Net Worth, Body Measurements, Marriage)
-

 Entertainment10 months ago
Entertainment10 months ago12 Online Streaming Sites that Serve as Best Alternatives to CouchTuner
-

 Apps10 months ago
Apps10 months agoThings you need to know about Marathi keyboard today
-

 Apps10 months ago
Apps10 months agoStuck with Your default Bangla keyboard? Isn’t it time for a change?
-
 Entertainment10 months ago
Entertainment10 months agoMovierulz Website: Movierulzz 2021 Latest Movies on Movierulz.com
-

 Social Media10 months ago
Social Media10 months agoBrooke Daniells: Everything About Catherine Bell’s Partner
