Guides
A Step-By-Step Guide To Writing An A+ Paper In No Time

‘Writing a paper can often feel like a daunting task – especially when you’re under pressure to get it done in a short period of time. But don’t worry, this step-by-step guide will show you how to write an A+ paper quickly and efficiently! From researching your topic to proofreading at the end, we’ll walk you through everything you need to know about writing an exceptional paper in no time. So let’s get started!
Overview: What is an A+ Paper?
An A+ paper is a well-written and well-researched piece of Dissertations Land that earns the highest possible grade. There is no one formula for an A+ paper, but there are some key elements that all successful papers share. In this guide, we’ll walk you through the steps to writing an A+ paper, from choosing a great topic to editing and proofreading your work. By the end, you’ll have everything you need to write an A+ paper in no time!
Step 1: Choosing a Topic
There are a few things to consider when choosing a topic for your papers. First, think about what you’re interested in and what you want to write about. It’s important to choose a topic that you’re passionate about, as this will make writing the paper much easier and more enjoyable.
Once you’ve chosen a general topic, it’s time to start narrowing down your options. Think about what aspect of the topic you want to focus on, and what specific angle you want to take with your papers. For example, if you’re interested in writing about the effects of climate change, you could narrow your focus to discussing how climate change is affecting marine life.
Once you’ve decided on a specific topic and angle, it’s time to start doing some research. Start by looking for reputable sources that contain information on your topic. Make sure to take note of any relevant statistics or data that you come across, as this will be useful when writing your paper. Once you have enough information, you can start outlining your paper and writing your first draft.
Step 2: Researching & Outlining
Now that you’ve gathered all of your materials, it’s time to start researching and outlining your paper. This step is crucial in ensuring that your paper flows smoothly and efficiently.
To begin, take a look at your research question and break it down into smaller, more manageable chunks. What are the key points you need to address? From there, you can start to develop a basic outline for your paper. Include an introduction, body paragraphs, and a conclusion.
Once you have a rough outline in place, it’s time to start filling in the details. Begin by conducting a thorough literature review of the existing research on your topic. This will help you better understand the current conversation surrounding your topic and identify any gaps in the literature.
As you’re reading through the existing research, take note of any particularly strong arguments or pieces of evidence that you can use in your own paper. Be sure to cite these sources properly as you’ll need to include them in your final draft.
Once you’ve finished your literature review, it’s time to start writing! Begin with a strong introduction that grabs the reader’s attention and gives them an overview of what they can expect from your paper. Then, move into each of your body paragraphs, addressing each point from your outline in turn. Use evidence from your literature review to support each point as needed. Finally, wrap up your paper with a strong conclusion that ties everything together and leaves the reader with something to think about.
Step 3: Writing the First Draft
Assuming you’ve followed the tips in Steps One and Two, now it’s time to start writing your first draft. Don’t worry about getting everything perfect at this stage – just get your ideas down on paper (or screen). Once you have a rough draft, you can start to edit and improve it.
To write a good first draft:
– Start with an outline of your main points. This will help you stay on track as you write.
– Write in short, simple sentences. You can elaborate and use more complex language in later drafts.
– Don’t worry too much about grammar or spelling at this stage – just get your ideas down. You can fix mistakes later.
– Keep going until you reach the end of your paper. It’s okay if you don’t have everything figured out yet – you can still revise and edit your paper later.
Step 4: Editing and Revising
Assuming you have followed the steps in this guide up to this point, you should now have a pretty solid first draft of your paper. But that doesn’t mean it’s perfect just yet. In order to take your paper from “good” to “great”, you will need to do some editing and revising.
Here are some tips for editing and revising your paper:
– Take a break from your paper after you finish writing the first draft. This will help you come back to it with fresh eyes and a new perspective.
– Read your paper out loud. This will help you catch any errors or awkward phrasing that you might not notice when reading silently in your head.
– Use a grammar checker like Grammarly or the built-in spelling and grammar checker in Microsoft Word. However, don’t rely on these tools completely – they can’t catch everything.
– Ask someone else to read your paper and give feedback. A second set of eyes can often spot things that you missed.
Once you’ve gone through and made all the necessary edits and revisions, congratulations! You should now have an A+ paper!
Step 5: Proofreading for Final Touches
Once you have your paper written, it’s time for a final read-through to make sure everything is in order. This step is important to catch any last minute errors or typos. After all, you don’t want your hard work to be marked down because of a few simple mistakes!
When proofreading, read through your papers slowly and carefully. Check each sentence for grammar and spelling errors. If you find any mistakes, fix them immediately. It can also be helpful to read your paper out loud. This can help you catch errors that you might not otherwise notice.
Once you’re satisfied with your paper, congratulations! You’ve now completed the steps needed to write an A+ paper in no time flat.
Conclusion
Writing an A+ paper can be a daunting task, but with our step-by-step guide, you’ll be able to confidently tackle any assignment. We hope that this guide has given you the tools and confidence necessary to write a high quality essay in no time. Take your time when writing, proofread thoroughly and use all of the tips provided here for best results. With these steps in mind, nothing is stopping you from getting that perfect grade!
Guides
What are the best ways to get a CSM Agile certification?

Businesses create Scrum teams, allowing team members to express themselves to improve their dynamic development processes. Scrum Masters help these teams deliver continual customer value. Enterprises require the best-certified scrum master. Aspirants should never overlook scrum master classes to obtain certification. Businesses create Scrum teams, allowing team members to express themselves to improve their dynamic development processes. Scrum Masters help these teams deliver continual customer value. Enterprises require the best-certified scrum master. In this post, let’s see the top ways to win CSM Agile certification.
Before becoming a Scrum Master, we must grasp what Scrum is and how it benefits the organization. Scrum is an Agile approach that helps teams tackle sophisticated, adaptable problems creatively and efficiently while maximizing product value. Scrum is reportedly easy to grasp but hard to master. Scrum is a framework that uses multiple procedures and strategies to create the best product.
What is the Certified Scrum Master course?
You may ask what scrum master certification is. Experts in Agile technique lead teams as Scrum Masters. A Scrum Master can boost a company’s success. CSM certification is required to become one. In addition, after obtaining Scrum Master certification, seeking SAFe certification is a strategic move. Scrum Masters with SAFe certification can negotiate difficult, large-scale Agile transformations. This dual certification strengthens leadership abilities, preparing professionals to guide Agile success not only at the team level, but also across whole companies.
The Scrum Alliance’s CSM certification is globally recognized. Professionals who pass the CSM exam and show Scrum terminology, practices, and principles receive this desired credential.
You may create items that improve people’s lives and promote optimism. More specifically, you may make a positive workplace for coworkers and maximize project success.
Obtaining the CSM Certification Process
After discussing the value of CSM certifications, we’ll examine how to get one. This certification has these prerequisites:
1. CSM certification eligibility
Anyone can start with Scrum Alliance’s basic CSM certification. Agile framework beginners who wish to learn Scrum should use it. Scrum may be used in many businesses and teams, so marketers, data analysts, HR experts, and others interested in agile can get certified.
You must complete a two-day Scrum Alliance-certified scrum trainer (CST) training course to receive this credential. Scrum basics, roles and duties, sprint planning, retrospectives, agile requirement analysis, prioritizing product backlogs, and scrum master competencies will be covered in this live and interactive training.
2. CSM certification exam overview
After two days of instruction, participants must pass an online exam to prove they understand Scrum. After completing the exam, participants become CSMs. An outline of exam expectations:
- 50 multiple-choice questions
- One-hour exam
- Minimum passing score: 7%
- Two free attempts
- Accessible in many languages
- Two-year certification validity
3. How much does CSM certification cost?
You must shell out approximately $400 to become a Certified Security Manager. Following the free trials, each further trial will cost $25. Renewal of the certification requirements is required every two years and costs $100.
Ways for top CSM certification courses
To get your CSM agile certification, you need a good training program that covers Scrum principles and practices. Excellent CSM certification training programs are listed below:
- Authorized Scrum Alliance training providers: The governing organization for certifications authorizes numerous training providers. Certified Scrum Trainers lead CSM training at these institutes.
- Agile and Scrum training institutes: Numerous institutes provide extensive CSM training. You can consider Simplilearn, which has the best trainers.
- Online training platforms: It provides CSM training for self-paced learners or those with scheduling constraints.
- Corporate training programs: Some companies provide in-house CSM training to improve Agile procedures.
Below are all the Scrum Master certification exam preparation methods:
- Scrum Plan
Certified Scrum professionals understand Scrum methodology and application. Starting the course requires time and effort, so you should have both. The certified Scrum Master course covers Startup, Attitudes and Abilities, Requirement Refinement, Planning and Protecting, and Adaptive Planning. Before taking the Scrum exam, you give yourself enough time to study.
- Read the Scrum guide
Learn Scrum via the Scrum Alliance. This includes sourcebooks and classroom resources on all Scrum topics. This underpins the Certified Scrum Master exam. When studying for the Certified Scrum Master test, use the Scrum guide to plan your efforts.
- Check Scrum ideas
You must understand four core ceremonies rather than the various Scrum terms and methods. Knowing these concepts and techniques will help you understand Scrum better.
- Sprints should last four weeks or fewer and be identical.
- Sprints should be continuous.
- A sprint should produce a marketable product.
- Comprehensively cover course
The CSM course includes PMI-ACP courseware for a year. You have enough time and material to prepare for the Certified Scrum Master test. Scrum and Agile concepts, values, and artifacts must be completed before the exam to ensure thoroughness. Before the exam, you should understand Scrum’s roles, rules, and agile procedures.
- Try Scrum Open assessment
Open evaluations and practice examinations are better CSM exam preparation ways. Select a few mock tests and improve your scores. Complete self-evaluation of your mock test performance will enhance your CSM exam preparation. CSM certification may allow several exam attempts.
- Learn Agile
Scrum is an Agile technique with four ideals and twelve principles. These ideals and concepts help the project team accept Agile project management. Agile methods will improve CSM concepts and CSM exam performance.
- Attend bootcamps and forums
You can also prepare for the Certified Scrum Master exam by talking to experienced peers. In such groups, professionals of various levels are preparing for the exam. Social networking is best for finding these communities. Contact trainers and CSM specialists for methodology and test preparation advice.
- Ensure idea retention
Beyond tests, Scrum ideas are essential. Linking topics to real-life situations can help you remember them till the exam. Known as mind mapping, applying curricular principles to real-world scenarios enables you to remember and use them. Scrum textbooks may include mind mapping.
End note
Enrolling in the right platform makes CSM certification easy. The certification is ideal for professionals who wish to lead and manage the Scrum Team. It’s the perfect time to develop job prospects across all Agile-implementing industries. Participants study the foundation of Scrum and the scope of Scrum roles in this course. The Scrum Alliance membership enables candidates to network with professionals worldwide and boost their industry.
Guides
EnglishWise: Unlocking the Path to Proficiency

Obtaining fluency in EnglishWise is of critical importance in today’s interconnected society. Learning English might be difficult, but it’s worth it in the end. This article delves into the complexities of studying English and offers advice on how to deal with the confusion and frustration that students often experience.
The Importance of English Proficiency
English competence offers doors to opportunity, from job progression to cultural enrichment. Learning English is a game-changer if you’re a student, a professional, or just someone who wants to open up more doors in life.
Common Challenges Faced by English Learners
Language Perplexities
The complexity of the English language, with its extensive vocabulary and sophisticated syntax, is a major barrier to its acquisition. A methodical strategy is required for navigating the linguistic complexities.
Tackling Burstiness in Learning
When students meet idiosyncrasies in their target language’s usage, they experience a burst in their learning since it is more difficult to anticipate patterns. Overcoming this burstiness demands dynamic tactics geared to real-life conditions.
Strategies for Overcoming Language Perplexities
Building a Strong Vocabulary
Expanding Your Vocabulary Vocabulary is the lifeblood of each language learner’s arsenal. Your vocabulary may be greatly expanded via the use of mnemonic devices, flashcards, and contextual learning.
Mastering Grammar Rules
Consistent practise is the best way to learn and internalise grammatical principles. Take part in practise sessions, tests, and practical applications to cement your understanding of English grammar.
Navigating Burstiness in English Learning
Immersive Language Practice
Put yourself in an environment where English is spoken and heard often. Expose oneself to several forms of language through media consumption.
Consistent Listening and Speaking Exercises
Overcoming impulsiveness requires consistent practise in both listening and talking. Participate in conversation, enrol in language-exchange programmes, and use digital tools to enhance your learning experience.
The Role of Context in Language Learning
Real-Life Conversations
Real-world discussions are when language truly shines. If you want to learn more about the culture and background of a language, try to have conversations with native speakers or language partners.
Cultural Understanding
The depth of your communication will increase as you study the cultural norms surrounding language use. Learn about different cultures by reading about and participating in their practises and literature.
Personalizing Your Learning Journey
Tailoring Learning Resources
Choose materials that relate to what you want to learn and how you want to grow as a person. Be fluent in both corporate and everyday English, and adjust your approach accordingly.
Setting Realistic Goals
Establish reasonable benchmarks to measure your progress. Maintaining motivation and making consistent progress over time is greatly aided by setting reasonable goals.
The Power of Active Engagement
Participating in Language Communities
Participating in linguistic communities encourages involvement. Creating supportive learning environments involves discussing language-related issues, seeking guidance, and sharing experiences.
Using Language Learning Apps
Use language-learning applications to take advantage of modern technologies. To keep your learning on its toes, these resources provide quizzes, challenges, and other interactive courses.
Overcoming Common Hurdles
Fear of Making Mistakes
Accept failures as opportunities to learn and grow. Fear of making errors can be a roadblock, but seeing them as chances to learn and improve can spur development.
Impatience in the Learning Process
Learning a new language takes time. Impatience is a major demotivator since it leads to frustration. Develop perseverance and relish interim successes.
Embracing a Growth Mindset
Adopting a growth attitude greatly aids the learning process. Keep in mind that you should hone mastery as a fluid ability by practising and gaining experience with each new obstacle.
Progress Tracking and Celebrating Achievements
Keep tabs on your development and recognise your successes, no matter how minor. Recognising your development keeps you motivated and devoted to your language learning goals.
EnglishWise: A Comprehensive Learning Solution
Learn how EnglishWise can help you succeed as an English learner by exploring this all-encompassing website. EnglishWise helps you reach new heights in your competence with individualised modules, instantaneous feedback, and engaging training.
Testimonials from Successful Learners
Hear from people whose lives have been changed by EnglishWise. Their achievements serve as examples of the platform’s potential and as proof of its success.
Conclusion
Beginning the path to English fluency calls for commitment, strategy, and support. Learners can succeed in their language-learning endeavours if they face the complexities and disruptions that they will inevitably encounter head-on.
FAQs
How long does it take to become proficient in English?
The time it takes to become fluent varies, but regular practise and total immersion might help you get there faster.
Can I learn English on my own without formal classes?
Absolutely. Self-study may be an effective strategy if time and effort are invested.
Is EnglishWise suitable for all proficiency levels?
Yes, EnglishWise is suitable for students of all skill levels.
What makes EnglishWise different from other language learning platforms?
EnglishWise is unique due to its customised learning experience, dynamic lessons, and immediate evaluation.
Guides
Understanding Gacha Sex in Gaming
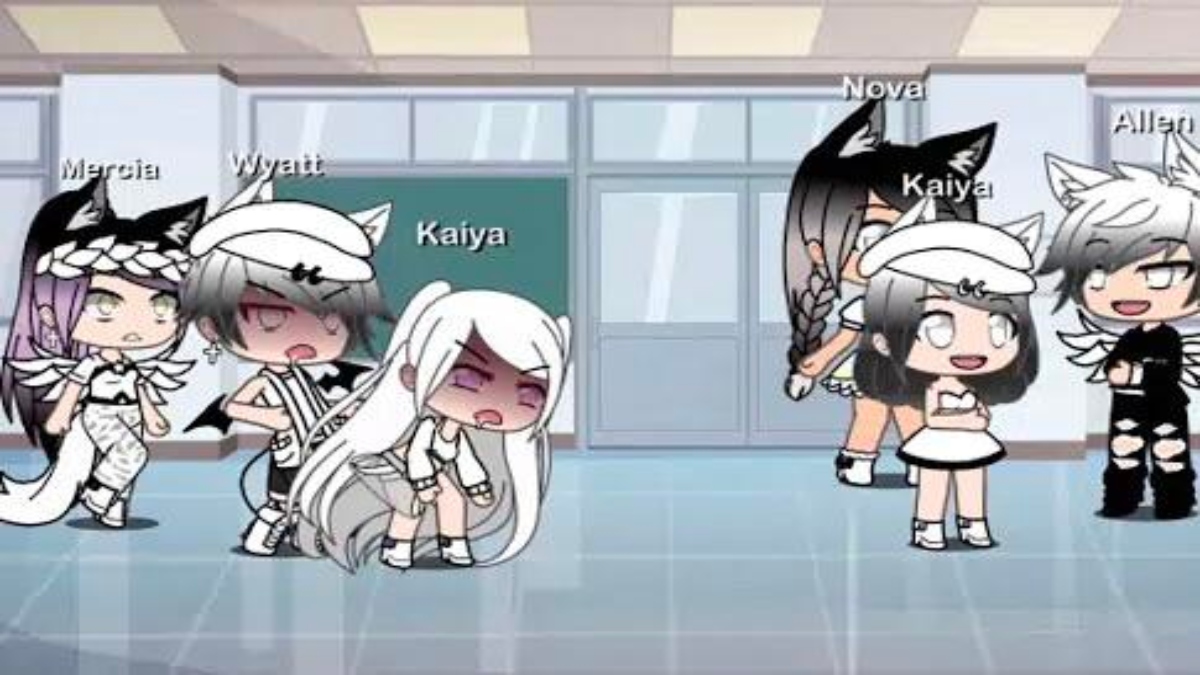

The game industry has changed drastically in the digital era. One of the most talked-about movements is the idea of “Gacha Sex.” The ramifications, debates, and effects of Gacha Sex on persons and relationships will be investigated in this article.
What is Gacha Sex?
Gacha Sex is a sexual activity named after the popular “Gacha Games.” You may get virtual things, personalities, and clothing in these mobile games by spending virtual cash on a random reward system. Gacha Sex, on the other hand, is shorthand for the sexy dialogue and behaviours that have become standard in these games.
Gacha Games: A Brief Overview
Theyare the bedrock upon which Gacha Sex is built, therefore familiarity with them is required before proceeding. These games provide players the possibility to take part in a purely random lottery experience. Gacha games are entertaining because their prizes are always a surprise.
The Controversy Surrounding Gacha Sex
A lot of parents, authorities, and gamers are worried about it. Opponents say it puts young people at risk of addiction and psychological damage by exposing them to violent and sexually explicit content. Gacha Sex has been called for regulation due to its graphic nature.
The Legal Aspects
Its borders are unclear from a legal sense. What is legal and what is not might be difficult to pin down because rules differ from country to country. There is already a lot of confusion about the topic, and this doesn’t help.
Risks and Concerns
It exposes young people to sexually explicit information, encourages behaviour similar to gambling, and can normalise sexual themes. The suddenness of this information might be distressing to gamers’ minds.
Gacha Sex and Its Impact on Relationships
The effects of it extend beyond the player. When one spouse gets preoccupied with Gacha Games to the exclusion of anything else, the relationship might suffer.
Recognizing Gacha Sex Addiction
Recognising the symptoms of it addiction early is key for addressing addiction issues. These symptoms include spending a lot of money on virtual products, isolating yourself from friends and family, and ignoring their duties.
How to Stay Safe
As a parent or player of Gacha Games, you may take precautions to avoid harm. Time limits, in-game purchase controls, and parental controls are all useful tools.
Regulation and Guidelines
There is a rising demand for industry-wide regulation and clear standards to limit the negative features of it. Players will be shielded from inappropriate material and monetary abuse in this way.
Parental Control and Responsibility
The gaming experiences of children rely heavily on their parents, who play a crucial role in keeping them safe. Parents should learn as much as they can about the games their kids enjoy so they can keep a close eye on them and establish appropriate limits for their use.
Positive Aspects of Gacha Games
Despite the criticism, Gacha Games do have some redeeming features. They foster critical thinking, originality, and problem solving. When played sensibly, they may provide hours of fun.
Conclusion
Gacha sex is a complicated problem in the game business. While there is potential for thrills and payoffs, there are also serious hazards, especially for younger players. The problems associated with Gacha Sex can be mitigated via education, ethical play, and regulation.
FAQs
1. What are Gacha Games?
In Gacha Games, the user spends virtual cash to randomly acquire in-game objects, characters, or clothing.
2. What is it?
Concerns about the influence of Gacha Games, especially among young people, have led to the term “Gacha Sex,” which describes the games’ graphic and sensual nature.
3. Is Gacha Sex regulated by law?
It is a confusing and difficult legal subject since its legislation differs from nation to country.
4. How can parents protect their children from its content?
Parents may limit their children’s gaming time, become familiar with the games their kids play, and utilise parental settings to keep their kids safe online.
5. Are there any positive aspects to it?
When played carefully and in moderation, Gacha Games can indeed aid in the development of these traits.
-

 Social Media10 months ago
Social Media10 months agoWho is Rouba Saadeh?
-

 Apps10 months ago
Apps10 months agoWhy is Everyone Talking About Hindi Keyboards?
-

 Social Media10 months ago
Social Media10 months agoMati Marroni Instagram Wiki (Model’s Age, Net Worth, Body Measurements, Marriage)
-

 Entertainment10 months ago
Entertainment10 months ago12 Online Streaming Sites that Serve as Best Alternatives to CouchTuner
-

 Apps10 months ago
Apps10 months agoThings you need to know about Marathi keyboard today
-

 Apps10 months ago
Apps10 months agoStuck with Your default Bangla keyboard? Isn’t it time for a change?
-
 Entertainment10 months ago
Entertainment10 months agoMovierulz Website: Movierulzz 2021 Latest Movies on Movierulz.com
-

 Social Media10 months ago
Social Media10 months agoBrooke Daniells: Everything About Catherine Bell’s Partner
